Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm
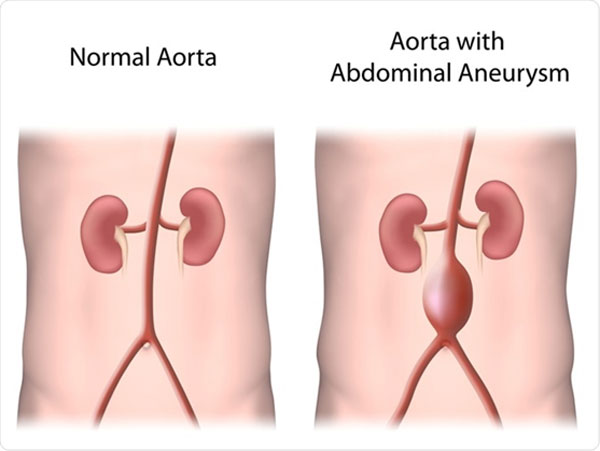
The aorta is the largest blood vessel in the human body. It carries blood from your heart up to your head and arms and down to your abdomen, legs, and pelvis. The walls of the aorta can swell or bulge out like a balloon if they become weak. This is called an abdominal aortic aneurysm (AAA) when it happens in the part of the aorta that’s in your abdomen.
You may also have an increased risk of developing AAA if you have a family history of it. If someone in your family has had an AAA, discuss this with your doctor and they may recommend an earlier screening.
There are other risk factors that you can do something about, like:
- controlling your blood pressure
- cutting down on alcohol
- giving up smoking
- keeping to a healthy weight
- lowering your cholesterol levels.
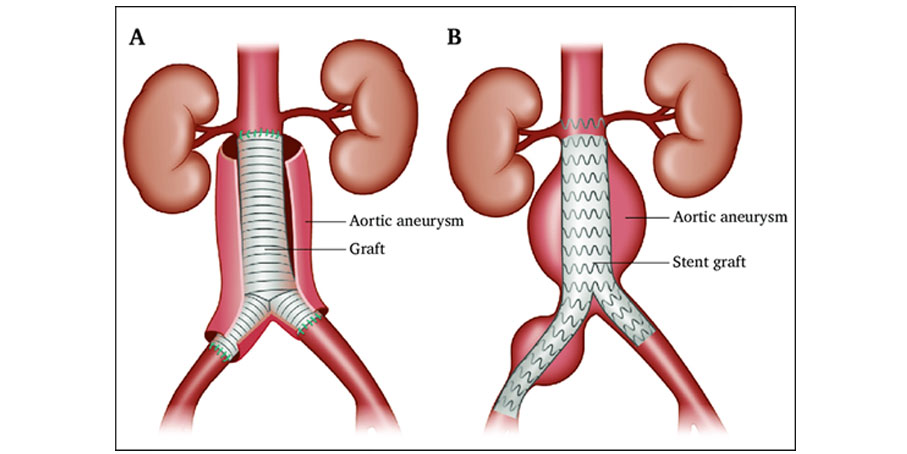
Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm (AAA) Open Repair
A large incision is made in the abdomen to directly visualize the abdominal aorta and repair the aneurysm. A cylinder-like tube called a graft may be used to repair the aneurysm.
What is endovascular grafting?
With endovascular stent graft therapy an endovascular stent graft is placed inside of your abdominal aorta to help protect the aneurysm from rupturing. incision. Instead, the doctor makes a small incision in the groin. He or she will insert special instruments through a catheter in an artery in the groin and thread them up to the aneurysm.
What is the difference between EVAR and TEVAR?
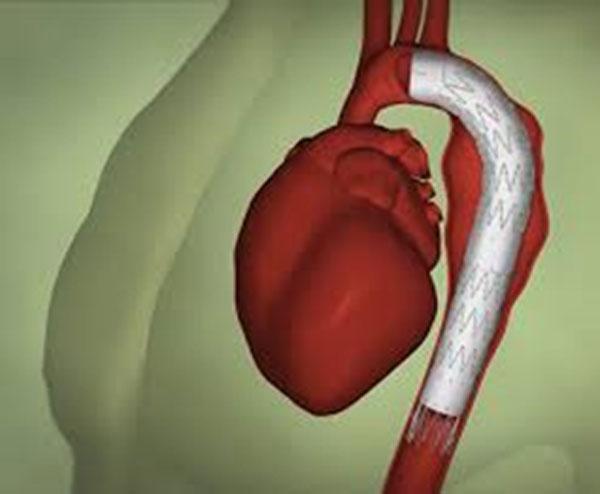
EVAR treats aneurysms in your abdomen (belly). Thoracic endovascular aneurysm repair (TEVAR) treats aneurysms in your thorax (chest). TEVAR is especially suited to treat aneurysms in your descending aorta – the part that moves down through your chest toward your belly.
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR)
Thoracic endovascular aortic repair (TEVAR) is a procedure to treat an aneurysm in the upper part of your aorta. The aorta is your body's largest artery. An aneurysm is a weak, bulging area in the aorta wall. If it bursts (ruptures), it can be deadly. TEVAR is a minimally invasive surgery.